Estimated Savings: > $250,000 in fraudulent credits and withdrawals prevented
Executive Summary
Cyvocate uncovered a critical flaw in a Web3-integrated payment system that allowed attackers to spoof blockchain payments without executing any real on-chain transaction. By forging responses from the blockchain API, malicious actors could have generated unlimited credits at no cost — leading to six-figure financial losses and irreparable reputational harm.
Our timely discovery and recommendations helped the client secure their verification pipeline, safeguarding user trust and protecting revenue.
The Challenge
Blockchain-based platforms rely on payment verification to maintain trust and integrity. In this case, the client’s system incorrectly trusted client-side blockchain responses instead of validating transactions server-side.
This oversight left the door open for attackers to fake successful payments — a fundamental breakdown in the payment logic that undermined the platform’s business model.
The Exploit Scenario
Through controlled testing, Cyvocate demonstrated how attackers could:
- Intercept the blockchain verification response.
- Forge the response to simulate a valid transaction.
- Submit the spoofed data to the platform.
- Receive account credits or token balances without ever executing an on-chain payment.
Illustration: Spoofed client response → Platform credits attacker account → No real blockchain transaction occurred
This loophole effectively allowed free money creation on the platform.
Proof of Concept
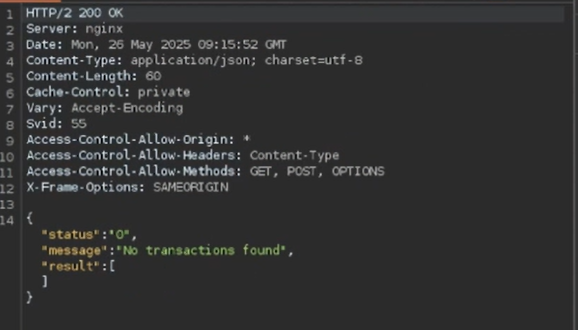
1. Captured Response
First, we intercepted the blockchain verification request. The platform accepted the following API response as proof of payment:
{
"status": "1",
"message": "OK",
"result": [
{
"blockNumber": "18954321",
"timeStamp": "1716720788",
"hash": "0xdecafbadbeef1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef1234",
"from": "0x[attacker_wallet]",
"to": "0x[platform_wallet]",
"value": "38912322754369850",
"txreceipt_status": "1",
"confirmations": "12"
}
]
}
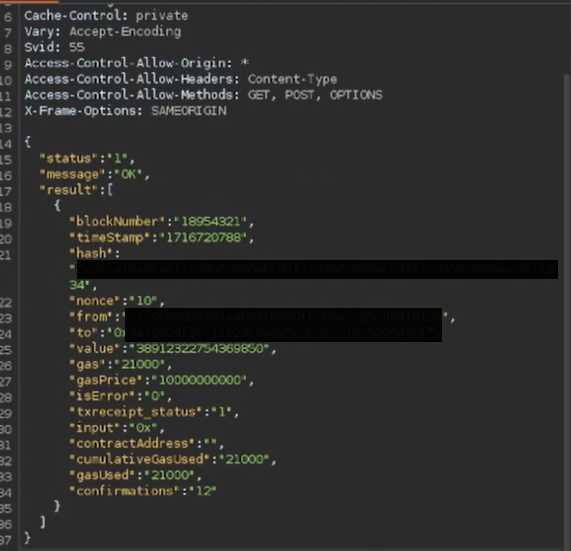
2. Forged Response
We then modified the verification response, changing the payment details to simulate a valid on-chain transaction without actually performing one.
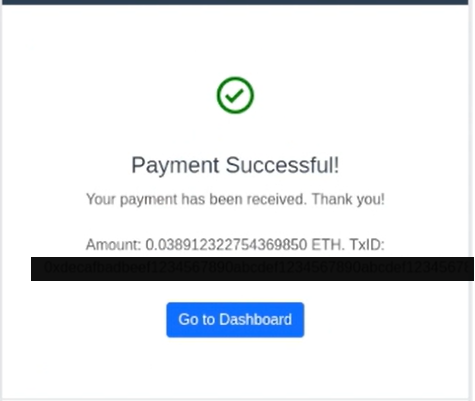
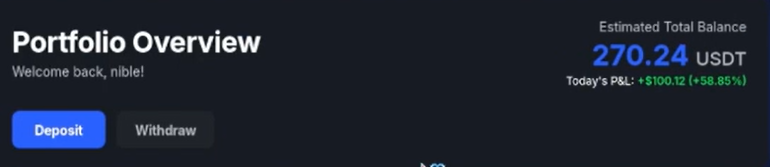
3. Confirmation of Spoofed Credit
After submitting the forged response, the platform credited the attacker account balance as if a real transaction had occurred.
Impact & Risks
The vulnerability posed severe risks to the platform:
- Direct Financial Losses → Attackers could generate credits or tokens at no cost.
- Trust Erosion → Payment systems are the backbone of user confidence; spoofing undermines platform credibility.
- Compliance Risks → Fraudulent on-chain transactions could bypass AML and anti-fraud monitoring.
Recommendations
CYVOCATE provided the following recommendations to secure the system:
- Server-Side Verification
- Validate all payments against the blockchain server-side.
- Correlate transaction hashes, sender addresses, recipient addresses, and values with the user’s request.
- Strict Validation Controls
- Reject any client-side provided verification data.
- Use confirmations from trusted nodes or third-party providers.
- Continuous Monitoring
- Log all payment events and flag anomalies (e.g., credits without matching on-chain transfers).
- Implement fraud detection to identify repeated spoofing attempts.